Navigating the Banking Cloud: Solutions, Regulations, and Optimal Applications

In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, the banking industry stands at the crossroads of innovation and security. Financial institutions grapple with the need to adapt to evolving communication channels, comply with rigorous regulatory standards, and safeguard sensitive customer data. In response to these challenges, this blog aims to explore the potential of cloud computing and conversational experiences as a transformative force in modern banking. We delve into the advantages that conversational AI on cloud offers to banks, ranging from cost savings to enhanced agility, and the various deployment models that can be leveraged. Moreover, we explore the significant regulatory guidelines that have shaped the adoption of cloud technology in the banking sector, including data residency and localization. Join us on this journey as we navigate the intricate path of banking in the cloud, offering insights into solutions, regulations, and optimal applications.
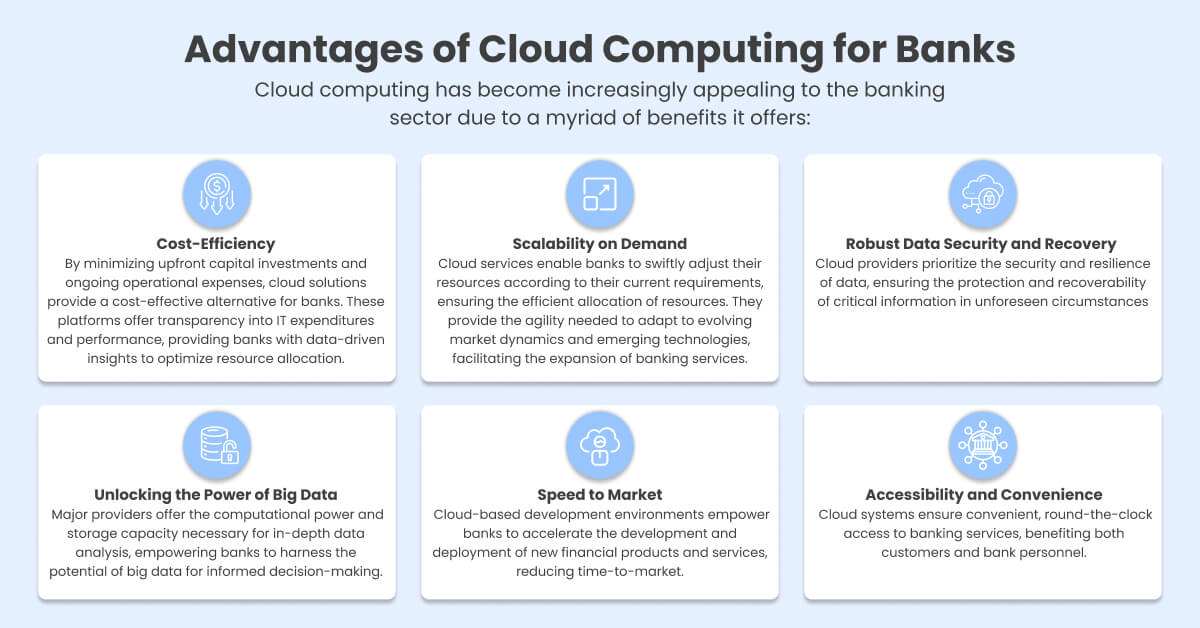
Understanding Cloud Deployment Models
- Private Cloud: Resources or infrastructure provisioned exclusively for a single organization comprising multiple users, which can be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or a combination of both, and can exist on or off-premises.
- Community Cloud: Resources or infrastructure exclusively available for a specific community of users from organizations that share common concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more organizations in the community, a third party, or a combination, and can exist on or off-premises.
- Public Cloud: Resources or infrastructure provisioned openly to the general public, with computing resources hosted by service providers at their own premises. Users do not have control or visibility over the infrastructure provided by the service provider.
- Hybrid Cloud: A composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology, enabling data and application portability, such as cloud bursting for load balancing between clouds.
Regulatory Guidelines by RBI and Other Bodies on Banks Regarding Hosting/Cloud
In recent years, regulatory guidelines have significantly influenced the approach of banks towards hosting and cloud services in India. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), along with other regulatory bodies, has issued several directives and recommendations that shape the banking sector’s adoption of cloud technology. These guidelines have played a crucial role in ensuring data protection, privacy, and security while encouraging innovation in the banking sector.
In 2013, the Reserve Bank of India encouraged banks to explore shared IT resources, including cloud computing, as a means to optimize costs while emphasizing the importance of ensuring privacy, confidentiality, security, and business continuity. Concurrently, IDRBT (Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology) introduced a Cloud Security Framework for the Indian banking sector. Since then, there has been a gradual increase in the adoption of cloud computing in the banking industry. Larger banks have embraced the private cloud model, while smaller banks, particularly cooperative banks, have explored reliable alternatives like the Indian Banks Community Cloud (IBCC). The RBI has actively promoted the hosting of Core Banking System on IBCC for urban cooperative banks by providing financial assistance.
In a survey by the IDRBT, the banking sector’s preference for specific cloud deployment models was found. Private and Community Cloud emerged as the favored choices among banks, as they offer greater control and security for organizations comprising multiple users.

(Source IDRBT)
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA-2023)
The introduction of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA-2023) is a significant development in data protection and privacy regulations in India. This legislation recognizes the importance of protecting personal data while allowing lawful processing for legitimate purposes.
Penalties for Breach: The Act imposes penalties for breaches, with a minimum penalty of 50 crore INR for non-compliance. Banks, as custodians of sensitive financial data, must adhere to these provisions to avoid penalties.
Data Protection Authority of India: The Act establishes the Data Protection Board of India as an adjudicating body to resolve disputes between data principles and data fiduciaries. Banks must be aware of this authority’s role in handling data-related disputes.
Gupshup’s Solution
Gupshup presents a secure conversational banking solution that caters to the unique challenges faced by financial institutions. Let’s delve into the core strengths of Gupshup’s offering:
- Access to Message Content: Gupshup respects user privacy and does not access the message content. WhatsApp employs end-to-end encryption, ensuring that messages, calls, and media are accessible only to the sender and recipient. This security feature applies to personal and business messaging, with a unique security code for each chat..
- Client and Integration Architecture: Gupshup’s WhatsApp Business Client, delivered in docker form, ensures end-to-end encryption for message exchanges. The integration architecture supports HTTP and HTTPS protocols, with sensitive data masking.
- Personal Data Handling: Gupshup ensures secure processing of personal data, whether stored on customer-managed systems or in a private VPC in the cloud for Gupshup-managed deployments.
- Data Residency: Gupshup also manages 2 data centers of its own, India & European Union, to ensure that the data resides within the country and all the regulatory guidelines are met. To address data sovereignty concerns, Gupshup empowers organizations by offering an installable application. This application can be deployed on private clouds, keeping the data entirely within the organization’s network. This approach circumvents the need for relying on public cloud services for AI and CX capabilities, ensuring data stays within the organization’s jurisdiction.
- Compliance and Security Standards: Gupshup maintains high levels of compliance, including ISO 27001 and the pursuit of SOC2 Type-1 and Type-2 compliance. Robust security measures, data backups, role-based authorization, and DLP systems further enhance data security. As a key channel partner, WhatsApp aligns with Gupshup’s dedication to privacy and security. The WhatsApp Business Platform, hosted by Meta, employs a combination of people, processes, and technology security systems to ensure the privacy and security of customer data. Certified under SOC 2, the platform undergoes regular penetration testing and adheres to strict governance standards, providing customers with the assurance of compliance with data protection laws and industry best practices.
In addition to Gupshup’s comprehensive approach to data security and privacy, a recent implementation with a leading Indian bank showcases the practical application of these principles in the financial sector. The beta test conducted for the bank allows customers to conveniently make EMI bill payments on WhatsApp using Razor Pay. This implementation uses Meta’s Cloud API to store and process WhatsApp data.
Hybrid: A feasible solution for banks
We have discussed the advantages of both cloud and on-premise solutions for banks, and it’s worth highlighting that a hybrid approach might be the most practical solution, especially in the context of the stringent regulatory norms that banks must adhere to.
- Regulatory Compliance: While the cloud offers many benefits, some data may be subject to location-based regulations or restrictions. Hybrid solutions ensure that sensitive customer information remains within the bank’s secure environment, reducing the risk of data breaches. At the same time, less sensitive operations can take advantage of the scalability and flexibility provided by the cloud, without compromising on data security. The hybrid model enables banks to retain full control over their most critical data.
- Business Continuity: Hybrid solutions offer a safety net for banks in terms of business continuity. In case of cloud service interruptions or outages, banks can continue their essential operations using on-premise infrastructure. This redundancy ensures that customers can access their services even during unforeseen cloud disruptions.
- Scalability and Cost Management: Hybrid models allow banks to optimize costs by allocating on-premises resources for their core operations while leveraging the cloud for scalable and flexible services. This ensures cost-efficient resource allocation, which is particularly valuable for smaller banks with limited budgets.
Which Banking Applications are Suitable for Cloud Deployment?
As banks navigate the complexities of modernizing their operations and adapting to the digital age, deploying various applications on the cloud has become an attractive and practical solution. However, there are some nuances around banking applications better suited for cloud.
Non-Critical Applications: Banks should consider starting with applications that are less critical in nature. Non-transactional and non-customer-facing applications, such as e-mail and e-learning platforms, can be good starting points. These applications often have lower data sensitivity and can serve as test cases for cloud adoption.
Mobile Employee Applications: Applications used by mobile employees, especially those involving activity and time record-keeping, are excellent candidates for cloud deployment. These applications typically generate a relatively small amount of data compared to the organization’s core databases and are updated infrequently, making them well-suited for cloud migration.
Time-Zone Sensitive Applications: Applications that operate in different time zones can leverage cloud resources more effectively. Cloud computing allows for resource optimization based on time, ensuring that applications are readily available when needed.
Based on these considerations, here are some of the banking applications that can be deployed on the cloud:
- Core Banking Solution (CBS): While migrating the entire CBS to the cloud may be challenging, certain components, such as KYC validation, credit rating processes, cash management, anti-money laundering regulatory compliance reporting, and more, can be transitioned to the cloud. These applications experience peak workloads at specific times of the day, making them ideal for cloud utilization.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Analytics: CRM applications that focus on customer servicing, analytics, and management can greatly benefit from cloud deployment. Multichannel access ensures no latency in accessing CRM services, and cloud computing is well-suited for the uniform workloads associated with analytics, data warehousing, and reporting.
- Mobile Banking and Digital Channels: With the proliferation of mobile banking applications and digital channels, cloud deployment simplifies the connection between these applications and the bank’s internal servers. This reduces overhead and ensures a seamless customer experience.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP applications for finance, accounting, and human resource management can be effectively deployed on the cloud. The cloud’s scalability and flexibility support efficient resource allocation for these critical functions.
- Internal IT Tools: Applications used for internal purposes, such as project management and bug tracking, can be deployed on the cloud to streamline internal processes.
Conclusion
It is evident that the potential for transformation is vast – the cloud presents an array of advantages for banks, from cost reduction to heightened security. It offers a framework for agility, scalability, and innovation, which are essential in an era of rapid technological evolution. Moreover, the regulatory environment plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of cloud adoption in the banking industry. In embracing the cloud and hybrid models that offer the best of both worlds, banks can effectively navigate the complexities of modernization while ensuring data privacy and compliance with stringent regulations.




